LinTO Platform STT (aka LinSTT) Automatic Speech Recognition
What is an ASR system?
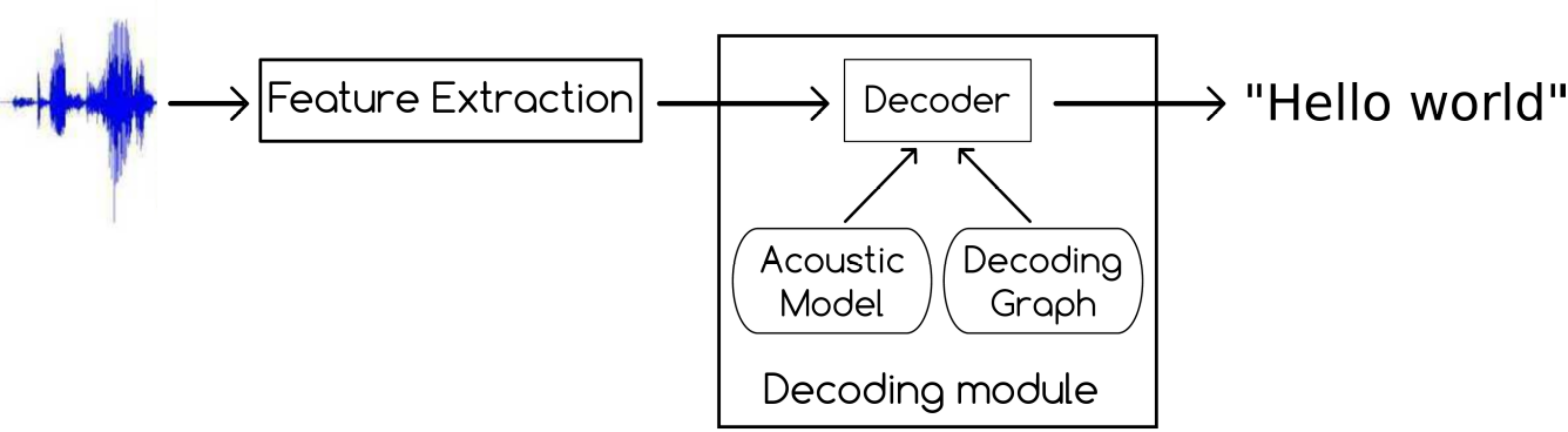
Generally, Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is the task of recognition and translation of spoken language into text. Our ASR system takes advantages from the recent advances in machine learning technologies and in particular deep learning ones (TDNN, LSTM, attentation-based architecture). The core of our system consists of two main components: an acoustic model and a decoding graph. A high-performance ASR system relies on an accurate acoustic model as well as a perfect decoding graph.
Main features
The main features of our speech-to-text transcriber are:
- Speech decoder using the recent advanced modeling technologies -- Deep Neural Networks.
- Compute the time stamp, i.e. the start and end time, for every word that was recognized.
- Perform the speaker diarization to assign speech signals to speakers engaged in dialog.
- The real number of speakers could be provided for high speaker diarization performance.
- Two output formats are allowed: a simple transcription using the Response Content Type
text/plain, or extended transcription with metadata usingapplication/json.
Acoustic Model
The Acoustic Model (AM) is used to represent the relationship between the speech signal and the phonemes that are basic units of sound acoustically realized in a language. Using an annotated speech corpus, this model is trained on a set of audio recordings and their corresponding transcripts.
You can find a description and a download link of the available models here: Acoustic Models
Decoding Graph
The Decoding Graph (DG) aims at capturing automatically the linguistic knowledge (syntax, semantics, etc.) about the target language from a large corpus text and helps to select the best option for a word transcription.
You can download the available graphs from here: Decoding Graphs